Table of Contents
- Why is it worth using migRaven.24 / 7 or the Consulting Service
- Why cleaning up is important when introducing an IAM
- Effectively clean up your Active Directory.
- Steps in the CleanUP process
- the following measures are worthwhile:
- Estimated effort for AD analysis and cleanup:
- Organizational requirements
- Technical requirements
Why is it worth using migRaven.24 / 7 or the Consulting Service
- Cleaning up historically grown AD environments
- Prepare Active Directory for the introduction of an IAM
- inexpensive alternative to complex domain migrations
- Outsourcing of parts of the company
- Merging of AD structures
- Handover of administration in the outsourcing project
migRaven.24 / 7 is a tool into which over 10 years of know-how from many projects has flowed. The specialists from the migRaven The development and advisory team have been looking for ways to first understand established Active Directory structures and then to clean them up. This is migRaven.24/7 analyzer possible.
Why cleaning up is important when introducing an IAM
An IAM system enables a high degree of standardization. This is achieved by automating processes. Unfortunately, most AD environments are not directly suitable for the introduction of an IAM.
The master data must be correct. Group nesting should be clean and, for example, only objects that are worth it should be passed to the IAM. This is exactly where the strength of migRaven.24 / 7 Analyzer: Obsolete objects can be reliably identified and eliminated. This is possible because the analysis is based on the powerful graph database. Graphs establish the connections between the objects. If there is no connection between objects, then the object is probably obsolete and can be deleted.
Only when this has been done should the technical implementation begin.
Effectively clean up your Active Directory.
Experience has shown that Active Directory structures are difficult to understand and manage with Microsoft's own resources. There is a high dynamic in large companies: new objects are created and deleted. The objects are regularly nested with one another, undocumented.
In environments with more than 250 accounts, this leads to constellations after a certain time that are difficult to understand and manage. A cleanup is necessary for reasons of cost and audit security.
Users and groups around Active Directory have been created to set security settings. If the group structures in AD are very complex, confusing and out of date, many security risks arise for your environment and make clean-up necessary. For example, over-authorizations can arise that grant unauthorized users access to sensitive data. For example, by going through several departments, trainees have access rights to almost all department directories.
This leads to the following questions:
- How can I get an overview of my current structure?
- How can the complex, confusing structures be cleared up?
An overview of the AD structures can be obtained with the migRaven.24 / 7 Analyzer can be obtained. MigRaven forms the basis for visualizing the current situation and at the same time provides the database for subsequent queries that are individually tailored to the customer's environment.
Graph database makes it possible
Behind migRaven.24 / 7 there is a powerful multi-tier architecture with an innovative database. This is designed to be able to analyze large AD environments with more than a million objects. (Relational databases are unsuitable for analyzing objects in the millions.) MigRaven therefore works with a fast neo4j graph database.
The main difference lies in the type of data storage. The structures are stored in a graph database in the form they exist in AD. These are complex networks with nodes that are directly related to each other. Because of this, data in a graph database can be analyzed much faster than that in a relations database.
In migRaven.24 / 7 Analyzer, the relevant data are displayed in different ways.
The following information is presented therein. They can be accessed by different users via different clients.
- Statistics on users, administrators, groups, nesting depths, token size, account credentials
- Lists of group nesting with effective members and memberships
- Orphan groups (a) (without members)
- Orphaned Groups (b) (Authorization groups not linked to an ACL)
- Redundant group nesting across users and groups
- User A -> Group1 -> Group2 -> Group3 -> ACE
- User A - [Connection x] -> Group2 -> Group3 -> ACE
- Role PreCheck: are used to plan future role groups on the basis of the current configurations
- RoleCrossChecks: Identification of incorrectly configured role groups through intelligent linking of information to account, groups and department
- Authorization analyzes
- Who is authorized where and via which channels
(Effective consideration of the authorizations:
- Who is authorized where and via which channels
ACE - Group - Group X - User
- Individual queries in the database based on special configurations on the customer side
The queries are available as standard reports or are developed according to requirements.
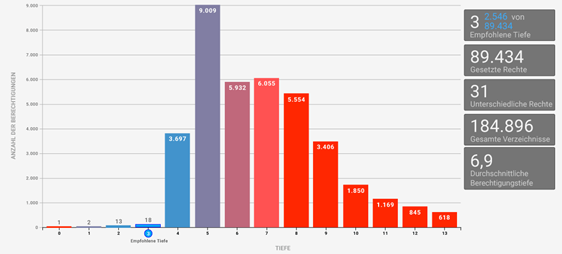
How can the complex, faulty structures be corrected?
Steps in the CleanUP process
- Understanding: Gathering important information in order to understand the current situation
- Optimization of the information: comparison of TARGET-IS, especially in the area of AD properties. E.g. Department ...
- Identification and removal of obsolete objects
- migRaven provides a basis for special reports on orphaned user accounts and groups
- Dissolution of redundant structures
- migRaven provides analyzes, reports and functions for the identification of redundant connections, whereby all effective connections are retained.
- Cleaning up circular and recursive group nesting
- By evaluating the account - group - department relationship in comparison to other accounts with similar or identical properties, incorrect configurations are revealed
- Flatten too deep, redundant group nesting
- Logical analysis of the structures based on graph theory
- Identification of possible solutions
The powerful functions of migRaven in combination with the experience of the specialists at aikux.com GmbH, find an individual and efficient solution for every AD cleanup.
the following measures are worthwhile:
- Number of groups and users and the group / user relationship is analyzed:
The two to three times the number of groups for user accounts is quite normal. Usually determined by the extensive management of NTFS directory permissions. If there are more, then it is definitely questionable. - Group nesting depth should never exceed 3 levels
Structures that are too deep are always a hindrance because they restrict the overview. Hierarchies usually have a negative effect because an object can only ever be in one place. Object properties can be assigned much more flexibly.
Max. 2-3 levels are optimal.
The following variants are ideal:
User -> Role group -> Authorization group -> (auxiliary authorization group)
User -> Authorization group -> (auxiliary authorization group)
Nesting role groups with one another may seem sensible at first glance. We strongly advise against this, because the overview is lost so quickly. - orphaned groups with no members should be deleted
Are mostly superfluous. - Orphaned permission groups that are not used in an ACL should be deleted
Obstruct the view and falsify the understanding of the actual situation. If a directory with expl. If permissions are removed, the associated group should be removed immediately.
migRaven can reliably show this immediately via a standard report. Often 20% -50% of all authorization groups can be deleted immediately. - Redundant group nesting should be broken because it leads to errors
deteriorate the clarity. - Redundant user group nesting
-> Permissions - Circular and recursive group nesting
must absolutely be resolved - Maximum group memberships of an account
the Kerberos token count plays an important role. An account can be in max. 1015 groups effectively be a member. For this reason, for example, superfluous group memberships must always be terminated immediately.
Estimated effort for AD analysis and cleanup:
The actual effort can vary greatly depending on the IT environment and the customer's goal and must therefore be determined individually. Talk to the consulting team from migRaven Academy.
Orientation parameters:
- Simplest form: 3-8 days for customers up to 1000 employees
- Large customers: 5-15 days
Including detailed documentation.
The effort for any subsequent AD CleanUp can only be estimated after the AD analysis.
Organizational requirements
In order to be able to organize the dates optimally, the following information should be made available in advance:
- Number of employees in the company?
- PC-relevant?
- Overview of locations
- Is an IDM / IAM in use?
- Number and which HR systems are in use?
- Administration responsibilities
- Are there automated processes for creating / modifying objects in the AD?
- Are roles used?
- How is the withdrawal of authorizations currently ensured? Least Privilege?
- Which domain level is there?
- Do trusts exist?
- The Wohler?
- How configured?
- Is there an OU concept in AD?
- Authorization concept in AD: are there delegated authorizations? Who has what rights?
- What group types are there security groups / distribution groups?
- Is there a naming concept for groups?
- how can one recognize the task of the groups? Are there suffixes / prefixes that suggest the use? Is there a description of the groups?
- Is there a naming concept for user accounts?
- Is there a naming concept for service accounts?
- Is there a process for building up the users and groups? Is this understandable?
- Documentation of all changes?
- Which group types are used? (DL / G / U)
- Which authorization concept is used? (AG-DL-P)
- Which tools are used for authorization management?
- What are the current processes for the administration?
- Are there data owners for the structures / objects?
- What types of people are there?
- Internal employees
- Trainee
- Accounts for temporary employees (external, students ...)
- System accounts
- What is the process like when dealing with accounts for external parties?
- Current handling of obsolete objects in AD
- Is there a process for deleting obsolete user objects? Will this be implemented?
- Are users deactivated or given an expiration date?
- Is there a process for deleting groups?
- Role groups
- Are there role groups?
- How can role groups be recognized?
- Is there a connection to the HR system that manages automatically?
- Are the properties maintained in the AD?
- How do you recognize (properties): department, function, location, superior, cost center?
- Target / actual comparison: Can the target values be exported from a system (HR) and compared with the actual values in AD?
- What other systems are there that are based on objects from the AD? (not with migRaven analyzable)
- Have a list created: Name / short description / owner
- E.g. SharePoint, databases, CRM systems ...
- it may be worth importing into migRaven via scripts
- Useful if customers are greater than 5000 users +
- Estimate, plan and communicate the effort (costs + time) for creating the script in advance
Technical requirements
- installation of migRaven for analysis
- Windows Server 2016+
- Sizing for migRaven according to customer environment
- Size AD: users / groups
- File system size: TB
- Storage space / RAM / HDD
- Checking the firewall settings for accessibility of the target system: typical Windows LDAP / SMB protocols
- Setting up the authorizations for reading out the authorizations of the FS
- Provision of a corresponding account
- Setting up the scans in migRaven
- If authorizations / roles from other systems in migRaven should be imported, then corresponding exports in CSV format

