Table of Contents
1. Need for list permissions
As a rule, access rights on NTFS file servers are granted lower than the first directory level. As soon as this is the case, you have to ensure that the user can browse through the file system to the corresponding directory. There are different options here with different effects.
2. Variants of the allocation of list rights
For browsing through the directory system can migRaven build flexible list permissions. There are basically two options available:
- Authorization groups are created for the list authorizations that, for example, include the "Change" authorization groups from the lower levels.
- In the directories under the list groups up to the explicitly authorized folder (authorization point = BEP), the authorization groups (of the BEP) are used for the assignment of the list authorizations.
The optimal way is the combination of both options. However, 1. it should not be used at levels that are too deep, otherwise the account will end up in too many groups. But position one must not be omitted because otherwise there will be too many entries in the ACLs of the upper directories. An ACL can hold a maximum of 1800 ACEs. Too many ACL entries make access to the directories slow.
3. List permissions - the technical structure
List authorizations should be assigned according to certain guidelines. On the one hand, the rule applies here that authorizations are only granted via groups, never directly (see: Direct permissions). In addition, the effectiveness of the permission should be limited to the appropriate folder. This is achieved by setting "Only this folder" to "Apply to":

Rights of a list group: corresponds to read-execute rights, but applied "Only to this folder"
4. List permissions in migRaven
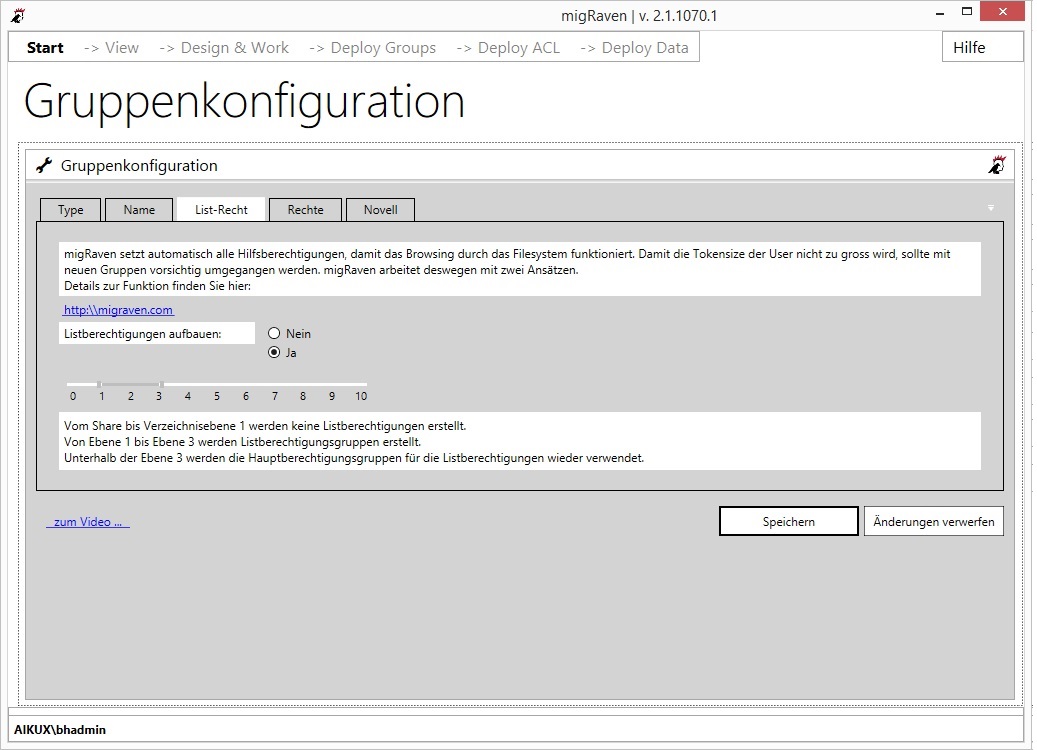
You can set where to create list groups or where to reuse the authorization groups of the authorization endpoint (BEP).
Automatic creation of list groups in the marked area (level 1 to 3 unterm Share). Below this, authorization groups (of the BEP) with list rights are automatically created up to the authorization point.
You can configure the values using the slider. The blue bar determines from which level and up to which level migRaven created separate list groups. Between 0 = Share and the left end of the blue bar will be from migRaven No list authorization established. From the right end of the bar to the explicit permission in the level you configured, the explicit permission groups are used to assign the list permissions.
- Level 0: No list rights are created.
- 1. to 3. Level: List authorization groups are generated which include the authorization groups (eg for Read and Modify) of the authorization endpoints.
- below the 3rd level: The authorization groups (eg for Read or Modify) of the authorization endpoint are reused, but only with list rights. Somewhat irritating is that these groups have suffixes like m, mx, or w, but only have list privileges above the BEP.
- For both types of groups: the rights are only applied to this folder. This means that at least one list group must be created for each level.
5. Effects using the example of a Modify right on the 7th level
To put it bluntly: such deep rights are not recommended. However, we often see access rights of this kind in our projects, often with rights structures that have evolved over time. So, what's bad or good about Modify Law on the 7th level?
- The account becomes a member of 4 groups in one fell swoop: one group for Modify, 3 groups for List –> Increase the TokenSize
- Setting the permissions on levels 1-3 is very quick because changes only occur in AD (group membership)
- Setting access rights from level 4 takes a very long time, depending on the number of files
- the number of ACEs in the ACL in levels 1-3 is low: good for perceived performance when accessing; more than 20 – 30 are noticeable
- the number of ACEs from level 4 may exceed the recommended number
It can with migRaven into the 10. Level automatically list permissions are established. The method is chosen so that it always cleans itself. Therefore, if a user is removed from a specific permission group for "modify", then the list permission is removed at the same time. If a complete authorization group for "Change" is deleted, the case 4, 5 and 6 remains in this case orphaned SID back. The list permissions of the levels 1-3 are completely clean.
6. Fazit
It is important to think about the points mentioned before setting up or redesigning the list authorizations and to weigh up the individual effects against each other. In principle, it is recommended to work with flat authorization structures because it significantly reduces the complexity of the problem, not only when assigning list authorizations. However, you can use authorization management software (e.g. 8MAN Enterprise) can also confidently comply with requests that require differentiated permissions and thus quickly go deeper than the 3rd or 4th level of a directory tree.
Talk to us if you have any questions about this topic!
- Step by step - the instructions for the cooperation between 8MAN and migRaven
- Video recommendation: Best Practice NTFS Permissions - The Great Webinar Recording!
Please comment on this amount with own experiences / opinions.